The Multiverse: Exploring Parallel Realities and Their Implications: A Critical Analysis of the Multiverse Concept and Its Philosophical Questions
The concept of the multiverse presents a fascinating framework for understanding how our everyday decisions might give rise to parallel realities. Initially proposed by the philosopher William James and later expanded through advancements in quantum physics, particularly Hugh Everett's Many-Worlds Interpretation, the multiverse theory challenges our conventional views on reality and consciousness. This analysis delves into the various facets of the multiverse concept, its relationship with quantum mechanics, and its broader philosophical implications.
Theoretical Foundations and Evolution
The multiverse theory, rooted in the idea that every decision creates a new parallel reality, offers a profound perspective on our actions and their consequences. William James introduced the notion, associating it with the multiplicity of interpretations of reality. This idea found a significant boost with the development of quantum mechanics in the early 20th century, thanks to the contributions of physicists such as Niels Bohr and Albert Einstein. Hugh Everett III's Many-Worlds Interpretation in the 1950s brought the concept into the scientific mainstream, proposing that all possible outcomes of quantum events occur in separate, parallel realities.
(Image: Hugh Everett III)
Quantum Mechanics and the Multiverse
Quantum mechanics, with its inherently probabilistic nature, provides a fertile ground for the multiverse theory. Schrödinger's famous thought experiment, involving a cat in a superposition of states, exemplifies the complexity of quantum phenomena and the notion of multiple coexisting realities. Everett's interpretation suggests that each quantum decision results in a branching of the universe, creating distinct versions where different outcomes materialize. This framework not only expands our understanding of quantum mechanics but also introduces profound questions about the nature of reality itself.
(Image: Schrödinger's cat illustration)
Philosophical and Ethical Implications
The philosophical implications of the multiverse are vast, touching on issues of free will, identity, and the nature of existence. If every decision spawns a new reality, then our understanding of choice and consequence becomes far more intricate. This notion challenges the traditional views of a singular, linear path of existence and introduces a complex web of possibilities. Furthermore, the ethical considerations become equally complex: if all possible outcomes occur, what does it mean for moral responsibility and accountability?
(Image: Philosophical thinking illustration)
Multiverse in Popular Culture
The multiverse theory has also permeated popular culture, particularly through science fiction and superhero narratives. Marvel movies, for example, explore parallel universes where characters experience different lives, capturing the imagination of audiences and prompting creative reflections on reality. These stories often grapple with the implications of parallel realities, such as alternate histories and divergent personal trajectories, thereby making the complex scientific theories more accessible and engaging for the general public.
(Image: Marvel multiverse illustration)
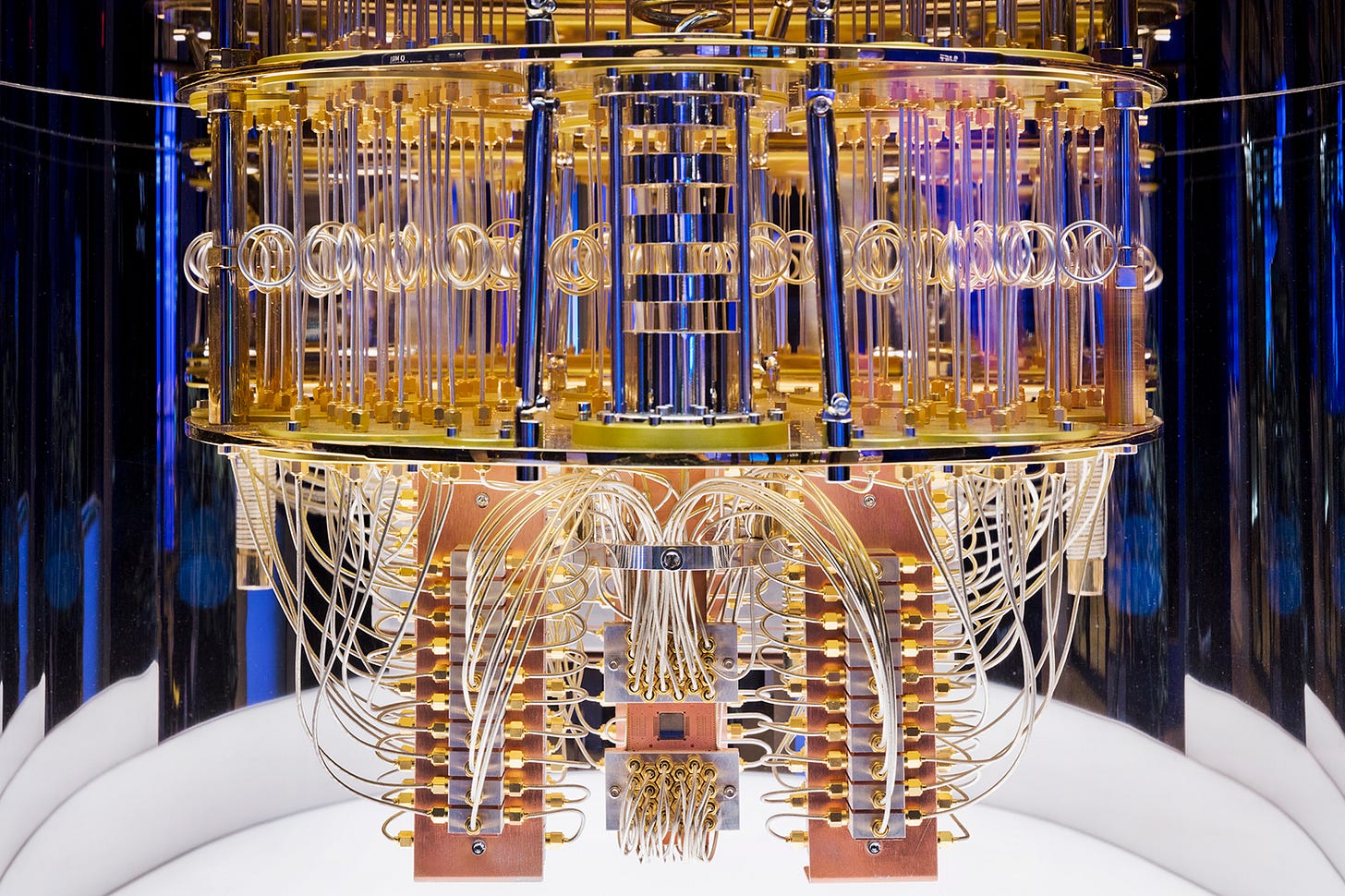
Scientific Exploration and Technological Implications
Modern advancements, particularly in quantum computing, have further explored the implications of the multiverse. Physicists like David Deutsch discuss how quantum computers might leverage resources from multiple universes, challenging our traditional understanding of computation and reality. This perspective opens new avenues for technological development and deepens our grasp of quantum mechanics' foundational principles. It also suggests that the multiverse concept is not just a theoretical curiosity but could have practical applications in shaping future technologies.
(Image: Quantum computer)
The Nature of Time and Reality
One of the intriguing aspects of the Many-Worlds Interpretation is its conception of time. It posits that all temporal states exist simultaneously across different realities, altering our conventional perception of time as a linear progression. This idea reshapes our understanding of temporal experience and prompts reconsiderations of how we perceive the flow of events in our lives.
(Image: Time and multiverse illustration)
Conclusion
The multiverse theory, with its rich blend of scientific, philosophical, and cultural dimensions, continues to provoke thought and debate. It challenges us to rethink our understanding of reality, consciousness, and the nature of existence. As our scientific knowledge and technological capabilities expand, the exploration of parallel realities will likely yield new insights and further blur the boundaries between the possible and the actual.
(Image: Universe and consciousness illustration)
This analysis underscores the enduring appeal and complexity of the multiverse concept, highlighting its significance in both scientific inquiry and philosophical discourse. It invites us to consider the broader implications of our daily decisions and the potential existence of countless parallel realities.
Subscribe to Our Substack! 📬
Stay informed and engaged with the latest updates, critical analyses, and insightful commentary on the hottest topics. By subscribing to our Substack, you'll be part of a community that values quality content and thoughtful discussion. Your support enables us to continue bringing you the best material. 🙌
Subscribe today and never miss an update! ✨
Thank you for being a valued member of our community! 🌟